- 多想拥你在我的怀里
- 却无法超越那距离
- 美好回忆渐渐地远去
- 盼望今生出现奇迹
- 无尽的想念
- 荒了容颜
- 无助的爱恋
- 从未改变
这是今天的旋律,,,,今生今世,遥不可及~
1 终端设备
终端是一种字符型设备,通常使用tty简称各种类型的设备
1.1 串行端口终端(/dev/ttySn)
串行端口终端 (Serial Port Terminal )是使用计算机串行端口连接的终端设备。计算机把每个串行端口都看作是一个字符设备。在命令行上把标准输出重定向到端口对应的设备文件名上就可以通过端口发送数据。
1.2 伪终端(/dev/pty/)
伪终端 (Pseudo Terminal )是成对的逻辑终端设备,并存在成对的设备文件。以telnet 为例,如果某人在使用telnet 程序连接到Linux 系统,则telnet 程序就可能会开始连接到设备ptyp2 上,而此时一个getty 程序会运行在对应的ttyp2 端口上。 当telnet 从远端获取了一个字符时, 字符就会通过ptyp2 、ttyp2 传递给getty 程序,而getty 程序则会通过ttyp2 、ptyp2 和telnet 程序返回“login: ”字符串信息。这样,登录程序与telnet 程序就通过伪终端进行通信。通过使用适当的软件,可以把两个或多个伪终端设备连接到同一个物理串行端口上。
1.3 控制台终端(/dev/ttyn,/dev/console)
如果当前进程有控制终端 (Controlling Terminal ),那么/dev/tty 就是当前进程的控 制终端的设备特殊文件。可以使用命令“ps ax ”来查看进程与哪个控制终端相连,使用命令 “tty ”可以查看它具体对应哪个实际终端设备。/dev/tty 有些类似于到实际所 使用终端设备的一个连接。
在Linux 系统中,可以在系统启动命令行里指定当前的输出终端,格式如下:
console=device, options //device 指代的是终端设备//options 指代对device 进行的设置,它取决于具体的设备驱动
2 终端设备驱动结构
终端设备驱动都围绕tty_driver 结构体而展开,一般而言,终端设备驱动应包含如下组成:
- 终端设备驱动模块加载函数和卸载函数:完成注册和注销 tty_driver,初始化 和释放终端设备对应的tty_driver 结构体成员及硬件资源。
- 实现tty_operations 结构体中的一系列成员函数:主要是实现open()、close()、 write()、tiocmget()、tiocmset()等函数
2.1 tty层次结构
Linux内核tty驱动结构包括tty 核心、tty 线路规程和tty 驱动,从用户获取数据之后,其发送数据的结构图如下:
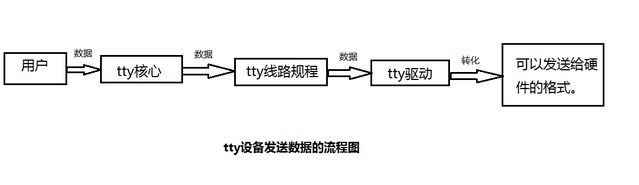
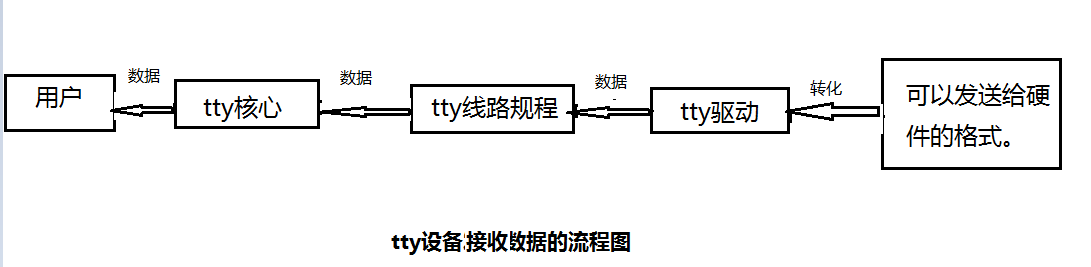
接收数据的流程图如下:
2.2 tty_dirver结构体
特定tty 设备驱动的主体工作是填充tty_driver 结构体中的成员,实现其中的成员函数,tty_driver 结构体的定义如下:struct tty driver { int magic; //表示给这个结构体的 “幻数 ”,设为TTY_DRIVER_MAGIC,在 alloc_tty_driver() 函数中被初始化。 struct cdev cdev; /* 应的字符设备cdev */ struct module *owner; /*这个驱动的模块拥有者 */ const char *driver name; const char *devfs name; const char *name; /* 设备名 */ int name base; /* offset of printed name */ int major; /* 主设备号 */ int minor start; /* 开始次设备号 */ int minor num; /* 设备数量 */ int num; /* 被分配的设备数量 */ short type; /* tty驱动的类型 */ short subtype; /* tty 驱动的子类型 */ struct termios init termios; /* 初始线路设置 */ //init_termios 为初始线路设置,为一个termios 结构体,这个成员被用来提供一个线路设置集合。 int flags; /* tty 驱动标志 */ int refcount; /*引用计数 (针 可加载的tty驱动) */ struct proc dir entry *proc entry; /* /proc 文件系统入口 */ struct tty driver *other; /* 仅 PTY 驱动有意义 */ ... /* 接口函数 */ int (*open)(struct tty struct *tty, struct file *filp); void (*close)(struct tty struct *tty, struct file *filp); int (*write)(struct tty struct *tty, const unsigned char *buf, int count); void (*put char)(struct tty struct *tty, unsigned char ch); void (*flush chars)(struct tty struct *tty); int (*write room)(struct tty struct *tty); int (*chars in buffer)(struct tty struct *tty); int (*ioctl)(struct tty struct *tty, struct file *file,unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg); void (*set termios)(struct tty struct *tty, struct termios *old); void (*throttle)(struct tty struct *tty); void (*unthrottle)(struct tty struct *tty); void (*stop)(struct tty struct *tty); void (*start)(struct tty struct *tty); void (*hangup)(struct tty struct *tty); void (*break ctl)(struct tty struct *tty, int state); void (*flush buffer)(struct tty struct *tty); void (*set ldisc)(struct tty struct *tty); void (*wait until sent)(struct tty struct *tty, int timeout); void (*send xchar)(struct tty struct *tty, char ch); int (*read proc)(char *page, char **start, off t off, int count, int *eof, void *data); int (*write proc)(struct file *file, const char user *buffer, unsigned long count, void *data); int (*tiocmget)(struct tty struct *tty, struct file *file); int (*tiocmset)(struct tty struct *tty, struct file *file,unsigned int set, unsigned int clear); struct list head tty drivers; }; 2.3 tty_std_termos结构体
驱动会使用一个标准的数值集初始化这个成员,这个数值集来源于tty_std_termios 变量,tty_std_termos 在tty 核心中的定义如下:
struct termios tty std termios = { _ .c iflag = ICRNL | IXON, /* 输入模式 */ _ .c oflag = OPOST | ONLCR, /* 输出模式 */ _ .c cflag = B38400 | CS8 | CREAD | HUPCL, /* 控制模式 */ _ .c lflag = ISIG | ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ECHOK | ECHOCTL | ECHOKE | IEXTEN, /* 本地模式 */ _ _ _ .c cc = INIT C CC /* 控制字符,用来修改终端的特殊字符映射 */ }; 2.4 tty_driver 结构体及tty 设备的操作
//1 分配tty 驱动 struct tty driver *alloc tty driver(int lines); // 这个函数返回 tty_driver 指针,其参数为要分配的设备数量,line会被赋值给 tty_driver 的num 成员//2 注册tty 驱动 int tty register driver(struct tty driver *driver); // 注册tty 驱动成功时返回0,参数为由alloc_tty_driver ()分配的tty_driver 结构体指针//3 注销tty 驱动 int tty unregister driver(struct tty driver *driver); // 这个函数与tty_register_driver ()对应,tty 驱动最终会调用上述函数注销tty_driver//4 注册tty 设备 void tty register device (struct tty driver *driver, unsigned index, struct device *device); // 仅有tty_driver 是不够的,驱动必须依附于设备,tty_register_device()函数用于注册关联于tty_driver 的设备,index 为设备的索引 (范围是0~driver->num )//5 注销tty 设备 void tty unregister device (struct tty driver *driver,unsigned index); // 上述函数与tty_register_device()对应,用于注销tty 设备//6 设置tty 驱动操作 void tty set operations(struct tty driver *driver, struct tty operations *op); // 上述函数会将tty_operations 结构体中的函数指针复制到tty_driver 对应的函数指针
3 设备的初始化和释放
3.1 模块加载和卸载函数
tty 驱动的模块加载函数中通常需要分配、初始化tty_driver 结构体并申请必要的硬件资源,下面举一个终端设备驱动的模块加载函数的例子,代码如下:
/* tty 驱动的模块加载函数 */ static int init xxx init (void) { ... /* 分配tty driver 结构体 */ xxx tty driver = alloc tty driver(XXX PORTS); /* 初始化tty driver 结构体 */ xxx tty driver->owner = THIS MODULE; xxx tty driver->devfs name = "tts/"; xxx tty driver->name = "ttyS"; xxx tty driver->major = TTY MAJOR; xxx tty driver->minor start = 64; xxx tty driver->type = TTY DRIVER TYPE SERIAL; xxx tty driver->subtype = SERIAL TYPE NORMAL; xxx tty driver->init termios = tty std termios; xxx tty driver->init termios.c cflag = B9600 |CS8 |CREAD |HUPCL | CLOCAL; xxx tty driver->flags = TTY DRIVER REAL RAW; tty set operations(xxx tty driver, &xxx ops); ret = tty register driver(xxx tty driver); if (ret) { printk(KERN ERR "Couldn't register xxx serial driver\n"); put tty driver(xxx tty driver); return ret; } ... ret = request irq (...); /* 硬件资源申请 */ ... } 3.2 打开与关闭函数
当用户对tty 驱动所分配的设备节点进行open()系统调用时,tty_driver 中的open() 成员函数将被 tty 核心调用。tty 驱动必须设置open()成员,否则,ENODEV 将被返回给调用open() 的用户。tty_struct 结构体被 tty 核心用来保存当前tty 端口的状态,它的大多数成员只被tty核心使用,驱动中可以定义一个设备相关的结体,并在open()函数中将其赋值给tty_struct的driver_data 成员,其代码如下:
/* 设备 “私有”数据结构体 */ struct xxx tty { struct tty struct *tty; /* tty struct 指针 */ int open count; /* 打开次数 */ struct semaphore sem; /* 结构体锁定信号量 */ intxmit buf; /* 传输 冲区 */ ... } /* 打开函数 */ static int xxx open (struct tty struct *tty, struct file *file) { struct xxx tty *xxx; /* 分配xxx tty */ xxx = kmalloc(sizeof(*xxx), GFP KERNEL); if (!xxx) return - ENOMEM; /* 初始化xxx tty 中的成员 */ init MUTEX (&xxx->sem); xxx->open count = 0; ... /* 使tty struct 中的driver data 指向xxx tty */ tty->driver data = xxx; xxx->tty = tty; ... return 0; } 4 数据发送和接收
用户在有数据发送给终端设备时,通过 “write()系统调用—tty 核心—线路规程”的层层调用,最终调用tty_driver 结构体中的write()函数完成发送。
4.1 tty_driver 的write()函数
tty_driver 的write()函数接受3 个参数:tty_struct、发送数据指针及要发送的字节数,一般首先会通过tty_struct 的driver_data 成员得到设备私有信息结构体,然后依次进行必要的硬件操作开始发送,相关的代码如下:
static int xxx write (struct tty struct *tty, const unsigned char *buf, int count) { /* 获得tty 设备私有数据 */ struct xxx tty *xxx = (struct xxx tty*)tty->driver data; ... /* 开始发送 */ while (1) { local irq save (flags); c = min t (int, count, min (SERIAL XMIT SIZE - xxx->xmit cnt - 1, SERIAL XMIT SIZE - xxx->xmit head)); if (c <= 0) { local irq restore (flags); break; } //复制到发送 冲区 memcpy (xxx->xmit buf + xxx->xmit head, buf, c); xxx->xmit head = (xxx->xmit head + c) &(SERIAL XMIT SIZE - 1); xxx->xmit cnt += c; local irq restore (flags); buf += c; count -= c; total += c; } if (xxx->xmit cnt && !tty->stopped && !tty->hw stopped) { start xmit (xxx);//开始发送 } return total; //返回发送的字节数 } 4.2 put_char()函数的write()替代
当tty 子系统自己需要发送数据到tty 设备时,如果没有实现put_char() 函数,write()函数将被调用,此时传入的count 参数为1,通过对以下代码的分析即可知。
int tty register driver (struct tty driver *driver) { ... if (!driver->put char)//没有定义put char()函数 driver->put char = tty default put char; ... } static void tty default put char(struct tty struct *tty, unsigned char ch) { tty->driver->write (tty, &ch, 1);//调用tty driver.write ()函数 } 4.3 tty_flip_buffer_push()范例
tty 核心在一个称为struct tty_flip_buffer的结构体中缓冲数据直到它被用户请求。因为tty 核心提供了缓冲逻辑,因此每个tty驱动并非一定要实现它自身的缓冲逻辑。如果其count 字段大于或等于 TTY_ FLIP BUF_SIZE ,这个 flip 缓冲区就需要被刷新到用户,刷新通过对 tty_flip_buffer_push()函数的调用来完成,其相关代码如下:
for (i = 0; i < data size; ++i) { if (tty->flip .count >= TTY FLIPBUF SIZE) tty flip buffer push (tty);//数据填满向上层 “推” tty insert flip char(tty, data[i], TTY NORMAL);//把数据插入 冲区 } tty flip buffer push (tty); 5 tty线路设置
5.1 线路设置用户空间接口
1) 调用用户空间的termios 库函数
用户空间的应用程序需引用termios.h 头文件, 头文件包含了终端设备的I/O 接口,实际是由POSIX 定义的标准方法。对终端设备操作模式的描述由termios 结体完成,通过tcgetattr() 、tcsetattr() 函数即可完成对终端设备的操作模式的设置和获取,这两个函数的原型如下:
int tcgetattr (int fd, struct termios *termios p); int tcsetattr (int fd, int optional actions, struct termios *termios p);
2) 对tty 设备节点进行ioctl()调用
大部分termios 库函数会被转化为对tty 设备节点的ioctl()调用,例如tcgetattr() 、 tcsetattr() 函数对应着TCGETS、TCSETS IO 控制命令。 TIOCMGET(获得 MODEM 状态位)、TIOCMSET (设置 MODEM 状态位)、TIOCMBIC(清除指示MODEM 位)、TIOCMBIS (设置指示MODEM 位)这 4 个I/O 控制命令用于获取和设置MODEM 握手,如RTS、CTS、DTR、DSR、RI、 CD 等。
5.2 tty 驱动的set_termios 函数
大部分 termios 用户空间函数被库转换为对驱动节点的 ioctl()调用,而 tty ioctl中的大部分命令会被tty 核心转换为对tty 驱动的set_termios()函数的调set_termios()函数需要根据用户对termios 的设置(termios 设置包括字长、奇偶校验位、停止位、波特等)完成实际的硬件设置。tty_operations 中set_termios()函数原型为:
void (*set termios)(struct tty struct *tty, struct termios *old);
5.3 tty 驱动的tiocmget 和tiocmset 函数
对TIOCMGET、TIOCMSET、TIOCMBIC 和TIOCMBIS IO 控制命令的调用将被tty 核心转换为对 tty 驱动 tiocmget()函数和tiocmset()函数的调,TIOCMGET 对应tiocmget()函数,TIOCMSET、TIOCMBIC 和TIOCMBIS 对应tiocmset()函数,分别用于取Modem 控制的设置和进行Modem 的设置,tty 驱动程序的tiocmget()函数范例如下:
static int xxx tiocmget (struct tty struct *tty, struct file *file) { struct xxx tty *info = tty->driver data; unsigned int result = 0; unsigned int msr = info->msr; unsigned int mcr = info->mcr; result = ((mcr &MCR DTR) ? TIOCM DTR : 0) | /* DTR 被设置 */ ((mcr &MCR RTS) ? TIOCM RTS : 0) | /* RTS 被设置 */ ((mcr &MCR LOOP) ? TIOCM LOOP : 0) | /* LOOP 被设置 */ ((msr &MSR CTS) ? TIOCM CTS : 0) | /* CTS 被设置 */ ((msr &MSR CD) ? TIOCM CAR : 0) | /* CD 被设置*/ ((msr &MSR RI) ? TIOCM RI : 0) | /* 振铃指示被设置 */ ((msr &MSR DSR) ? TIOCM DSR : 0); /* DSR 被设置 */ return result; } 5.4 tty 驱动的ioctl 函数
当用户在tty 设备节点上进行ioctl(2)调用时,tty_operations 中的 ioctl()函数会被 tty 核心调用。如果 tty 驱动不知道如何处理传递给它的 ioctl 值,它返回 ENOIOCTLCMD ,之后tty核心会 行一个通用的操作。tty 驱动程序的ioctl()函数范例代码如下:
static int xxx ioctl(struct tty struct *tty, struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) { struct xxx tty *info = tty->driver data; ... /* 处理各种命令 */ switch (cmd) { case TIOCGSERIAL: ... case TIOCSSERIAL: ... case TIOCSERCONFIG: ... case TIOCMIWAIT: ... case TIOCGICOUNT: ... case TIOCSERGETLSR: ... } ... }
版权所有,转载请注明转载地址: